

But those that addor delete three nucleotides have little or no effect. Length‑altering mutations thatadd or delete one or two nucleotides have severe defective phenotype (theychange the reading frame, so the entire amino acid sequence after the mutationis altered.). Results of combinations offrameshift mutations show that the code is in triplets. 64 different combinations offour nucleotides taken three at a time).Ģ. With three nucleotides, the set of allcombinations can encode If a codon were two nucleotides, theset of all combinations could encode onlyĬ. 20 amino acids are encoded bycombinations of 4 nucleotidesī. Three is the minimum number ofnucleotides per codon needed to encode 20 amino acids.Ī. tRNAs serve as anadaptor for translating from nucleic acid to proteinġ. The machinery for synthesizing proteins under the directionof template mRNA is the ribosome. it "speaks the language" of nucleic acids at one end and the"language" of proteins at the other end. A charged tRNA has an amino acid at oneend, and at the other end it has an anticodon for matching a codon in the mRNA ie. The adaptor molecule fortranslation is tRNA. Since there are 64 combinations of 4 nucleotides taken threeat a time and only 20 amino acids, the code is degenerate (more than one codon per amino acid, in mostcases). Eachgroup of three nucleotides encodes one amino acid. The nucleotidetriplet that encodes an amino acid is called a codon.
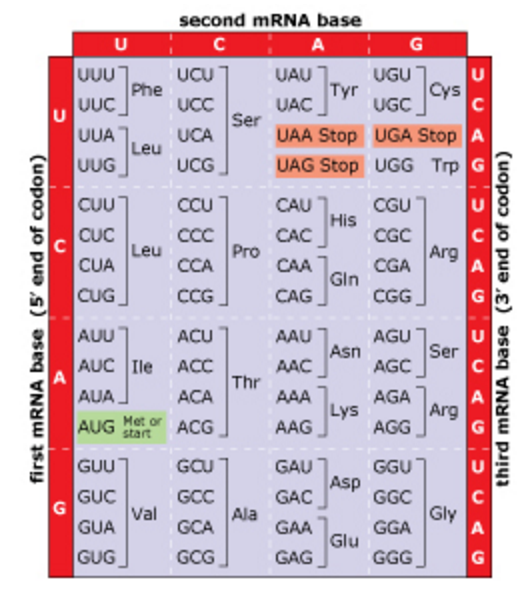
This demonstrated that the coding unit is 3nucleotides.

Experiments testing the effects offrameshift mutations showed that the deletion or addition of 1 or 2 nucleotidescaused a loss of function, whereas deletion or addition of 3 nucleotidesallowed retention of considerable function. The rules for translatingfrom the "language" of nucleic acids to that of proteins is the geneticcode. It must be translated into the encodedprotein. But the mature mRNA is not yet functional to the cell. Oncetranscription and processing of rRNAs, tRNAs and snRNAs are completed, the RNAsare ready to be used in the cell ‑ assembled into ribosomes or snRNPs andused in splicing and protein synthesis. Overview for Genetic Code and Translation:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
